Archives
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2019-06
- 2019-05
- 2019-04
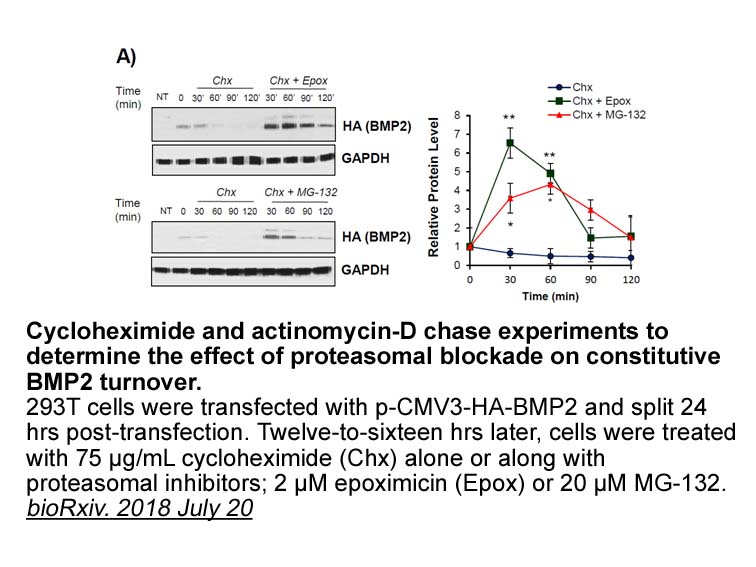
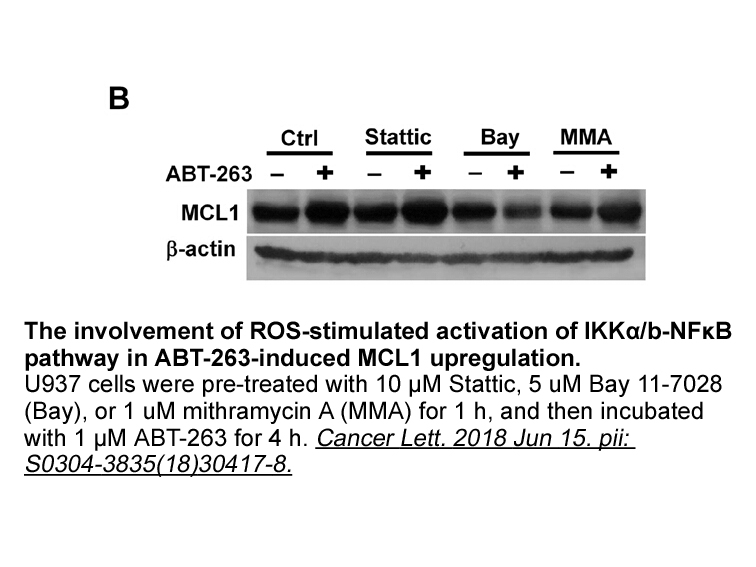
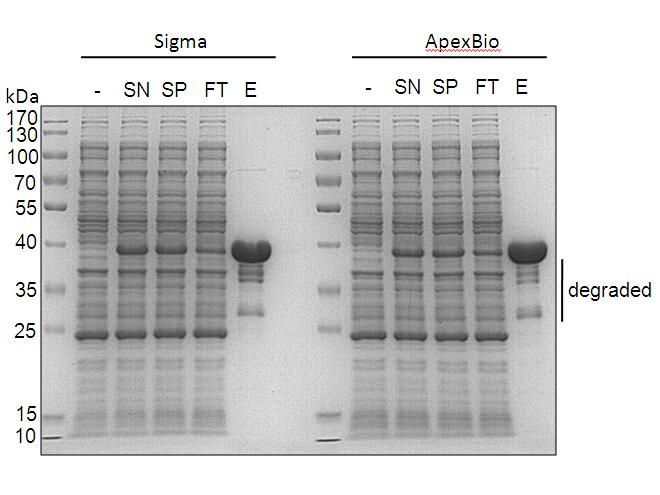
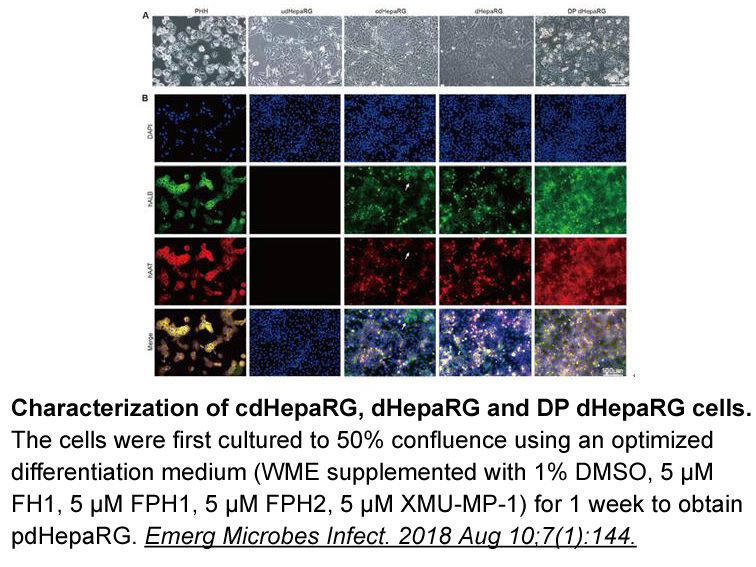
- 2018-07
-
NMS-873 receptor Several extragenic cot ts suppressors have
2021-01-11
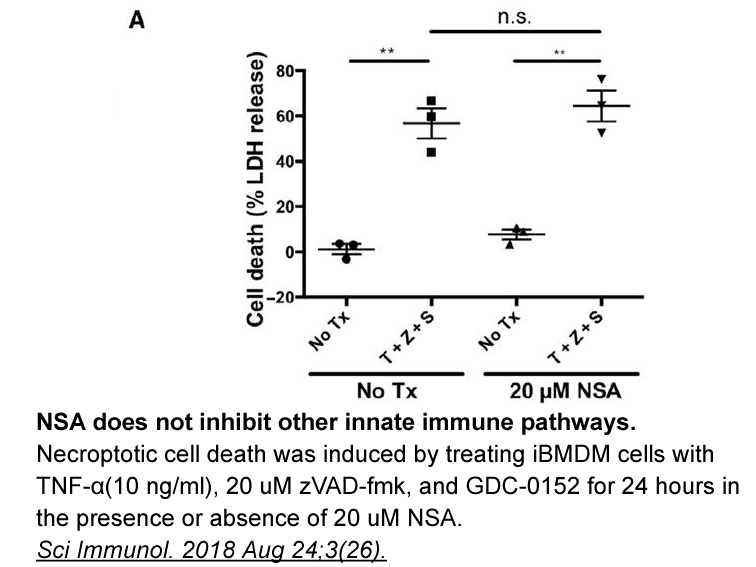
Several extragenic cot-1 (ts) suppressors have been identified. Among them, cytoplasmic dynein, dynactin, and nuclear distribution mutants of N. crassa, as well as an additional gene gul-1 (NCU01197), have been shown to have genetic interactions with cot-1 (Bruno et al., 1996, Seiler et al., 2006, T
-
T helper Th cells play a central role
2021-01-11
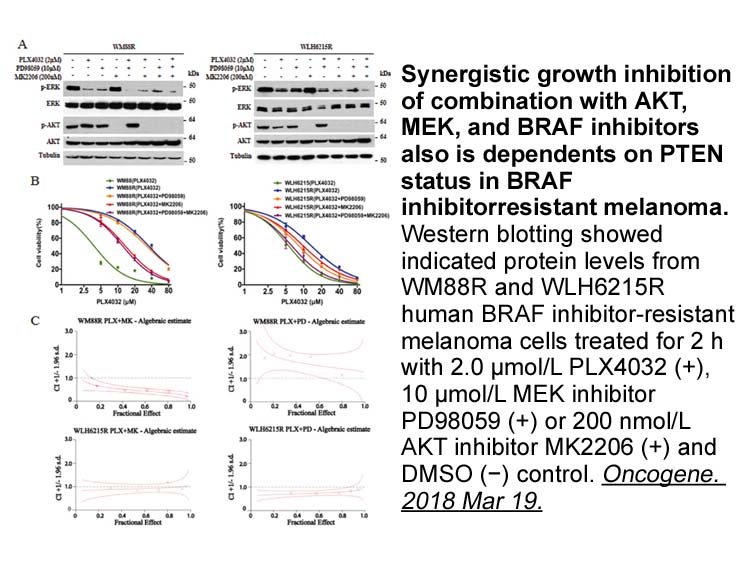
T helper (Th) SCH772984 play a central role in activation of immune system against infectious agents through secretion of lymphokines or cytokines. African trypanosomes target the Th cells and alter their activation, possibly for their own survival and perpetuity (Namangala, 2011). Trypanosoma bruc
-
We hypothesize that both IGF dependent kinase activation
2021-01-11
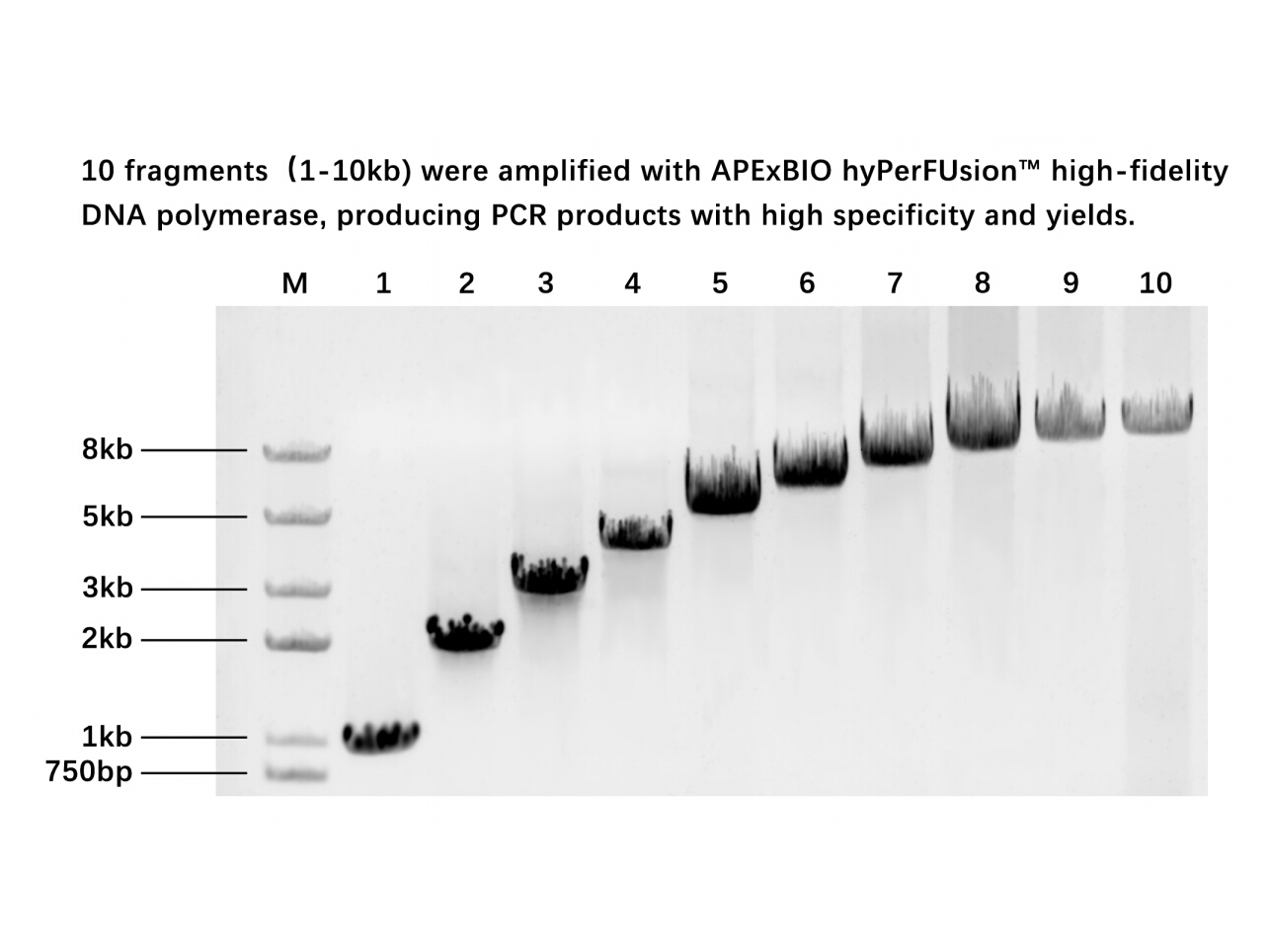
We hypothesize that both IGF-1-dependent kinase activation and locally synthesized neuroestrogens interactively regulate estrogen receptor activity in neuronal Asiaticoside synthesis in the absence of exogenously applied estradiol. The Neuro-2A cell line was chosen as the model system for these stu
-
Finally naringin and hesperidin have different glycosidic mo
2021-01-11
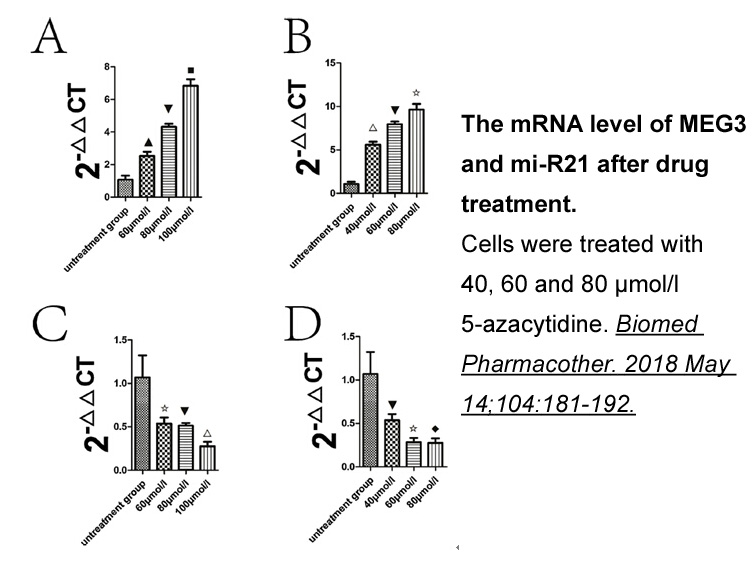
Finally, naringin and hesperidin have different glycosidic moieties (neohesperidose α-1,2 and rutinose α-1,6 respectively), bound in the same C7 position on the A ring of the flavonoid. The higher value of k/KM of RHA-Phis towards the former substrate suggests that the enzyme shows a preferential hy
-
br Enzyme catalysis A biochemically spontaneous process
2021-01-11
Enzyme catalysis A biochemically spontaneous process proceeds in a direction where free VER155008 mg of the system decreases. However, every spontaneous or energetically favorable reaction needs to overcome an energy barrier known as the activation energy barrier because of the formation of an u
-
PKA signalling in the nucleus was
2021-01-11
PKA signalling in the nucleus was thought to be due to the translocation of the catalytic subunit upon activation from the ML347 to the nucleus via diffusion [72]. However, a new understanding has emerged, as both the regulatory and catalytic subunits have been identified in the nucleus and functio
-
br Introduction The Epstein Barr virus induced gene EBI
2021-01-11
Introduction The Epstein–Barr virus induced gene 2 (EBI2 also known as GPR183) is a G protein-coupled seven-transmembrane (7TM) receptor that is predominantly expressed in B and T cells [1,2]. It regulates the trafficking of AZD 6244 within lymphoid tissues and is highly important for the genera
-
E protein was studied using specific anti E antibodies in
2021-01-09
E1 protein was studied using specific anti-E1 23 mg in wild type cells and in transfected cells overexpressing the enzyme. The results revealed several unusual characteristics, which are unique to this ubiquitin-activating enzyme. The E1 was translated as a full-length protein and then quickly prote
-
br Introduction The ubiquitination status of a target protei
2021-01-09
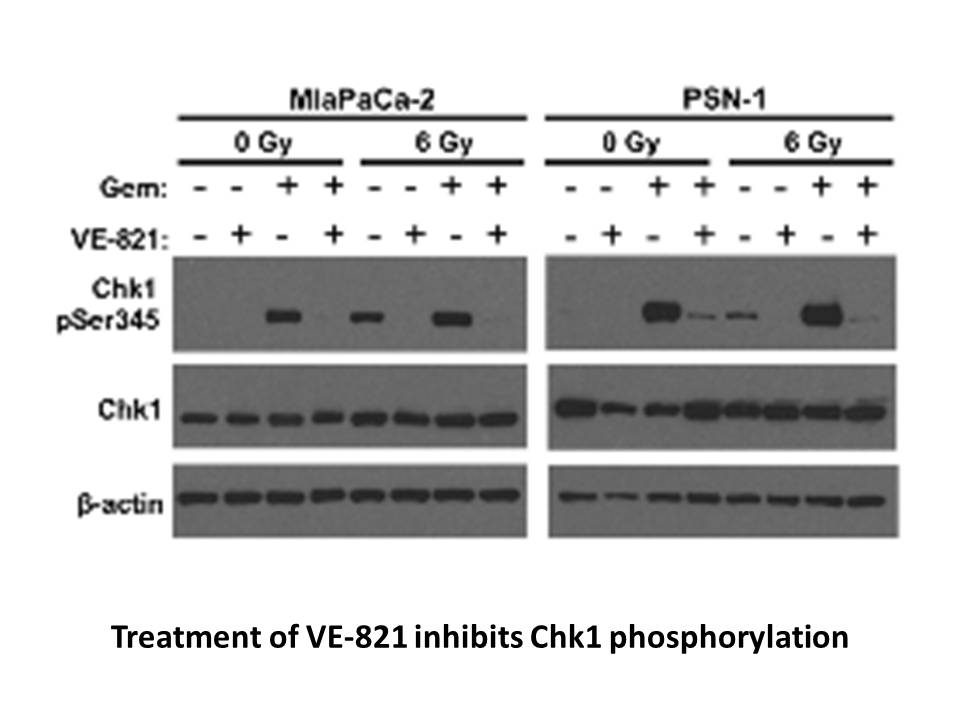
Introduction The ubiquitination status of a target protein is achieved via a delicate balance between two opposing forces: ubiquitin E3 ligases and DUBs. It has been postulated that the majority of proteins in a cell are regulated and modified by ubiquitin at some point (Hershko and Ciechanover,
-
br Other factors regulating DNA
2021-01-09
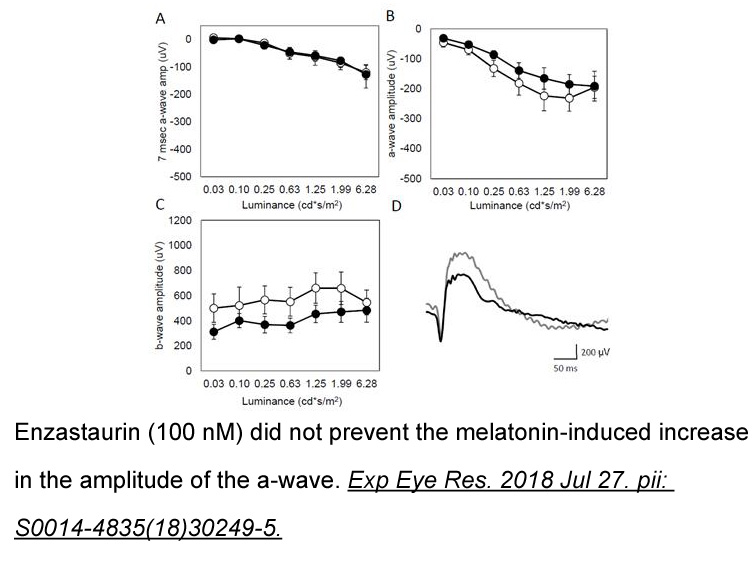
Other factors regulating DNA-PKcs Recent work in the field has also focused on factors that regulate NHEJ and NHEJ factors, in particular proteins that modulate DNA-PKcs. In this section we will highlight a number of factors which have been found to regulate DNA-PKcs. DNA-PKcs phosphorylation at
-
There are a few visible DNA staining methods which
2021-01-09
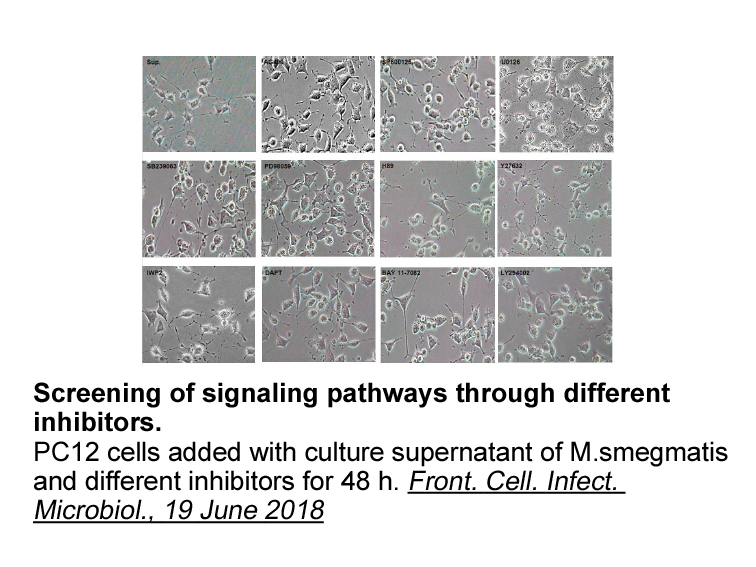
There are a few visible DNA staining methods, which use dyes such as methylene blue, brilliant cresyl blue [7], crystal violet [8], Nile blue [9], [10] and ethyl violet [11]. However, although safe, these methods require long staining times, lack sensitivity and are not specific for nucleic acids.
-
br DGKs inhibition and signaling Local DAG levels are
2021-01-09
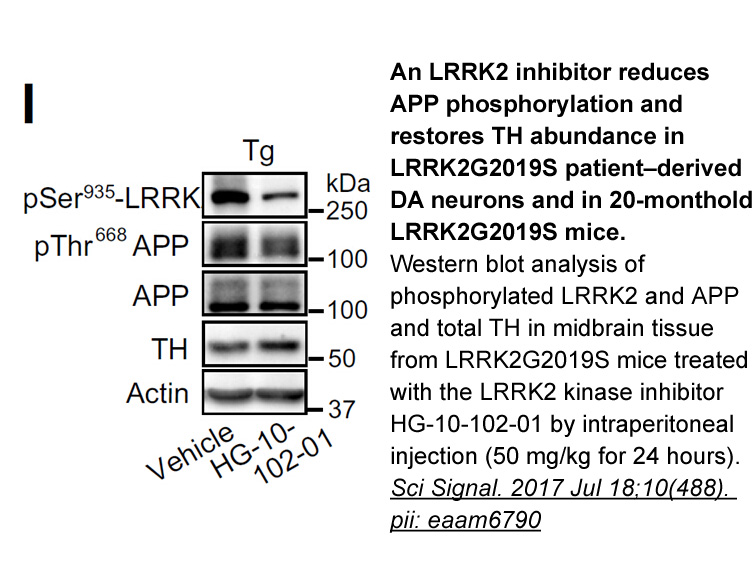
DGKs inhibition and signaling Local DAG levels are strictly controlled by a balance between synthesis and degradation rates. Both receptor controlled PLC-mediated production and DGK-mediated degradation are classically implicated in the control of “signaling” DAG. However, this dogma is starting
-
In this review focusing on biocatalyst formate dehydrogenase
2021-01-09
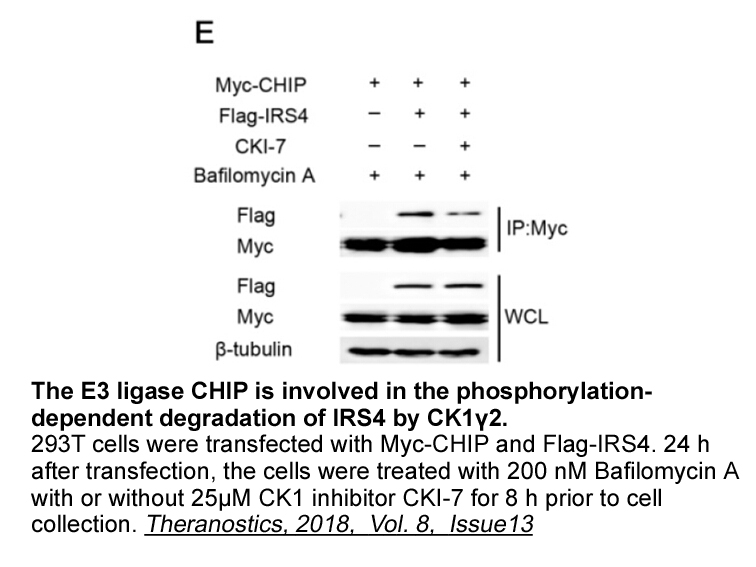
In this review, focusing on biocatalyst “formate dehydrogenase FDH” catalyzing both of the formic Galanthamine oxidation to CO2 and the CO2 reduction to formic acid, representative examples of properties, types, structure of active-site of FDH and, reaction mechanism of formic acid oxidation and CO
-
By using the C elegans Matrisome Annotator tool
2021-01-09
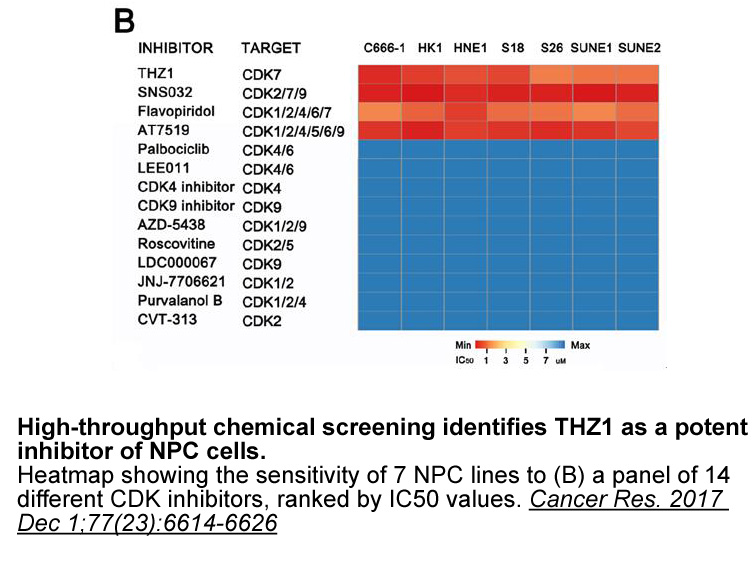
By using the C. elegans Matrisome Annotator tool, we found substantial enrichment for matrisome Ro 31-8220 in these data sets. Thus, re-analyzing -omic datasets with the C. elegans Matrisome Annotator tool may be useful to generate novel hypotheses about the role of the C. elegans matrisome for var
-
The cyclin dependent kinase deactivation is
2021-01-09
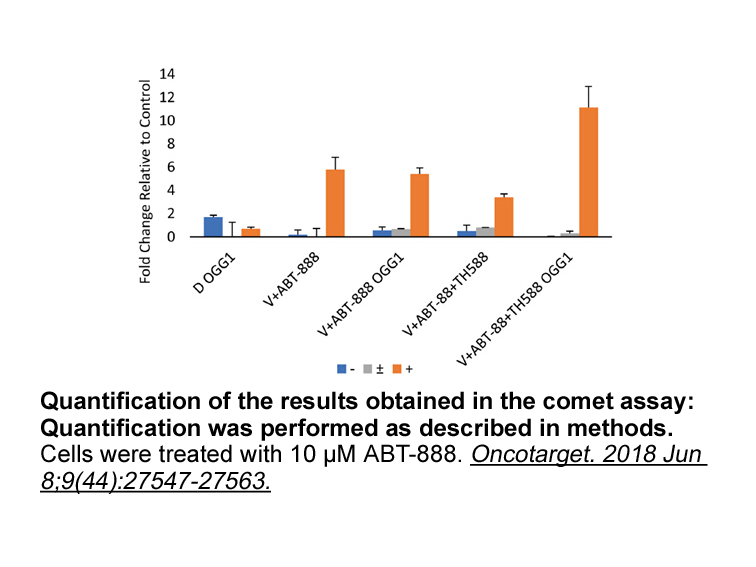
The cyclin-dependent kinase deactivation is carried out by a particular group of proteins cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CDKIs). These group of proteins blocks kinase activity by interfering with the interaction of cyclin-CDK complex [43]. The inhibition of CDK naturally occurs during a G1 phas
15809 records 723/1054 page Previous Next First page 上5页 721722723724725 下5页 Last page